Indian health-tech company Niramai to develop an AI-based computer-aided software for controlling spread of river blindness
Indian health-tech company Niramai will develop an AI-based computer-aided solution for controlling spread of river blindness. Niramai will leverage its innovative Thermalytix™ technology to detect the presence of live adult worms of Onchocerciasis which causes river blindness and significant disability.
Thermalytix is an automated diagnostic tool that combines thermal imaging with artificial intelligence to detect early stage breast cancer. This innovative non-invasive detection method is expected to help assess the efficacy of new drugs being developed to control the disease by killing the adult worms, potentially accelerating the elimination of river blindness, which today infects about 17 million people in Africa. This project is being supported by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation.
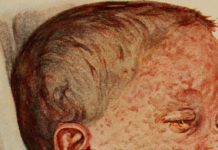
According to WHO, Onchocerciasis is an eye and skin disease caused by a worm (filaria) known scientifically as Onchocerca volvulus. It is transmitted to humans through the bite of a blackfly (simulium species). These flies breed in fast-flowing streams and rivers, increasing the risk of blindness to individuals living nearby, hence the commonly known name of “river blindness”. Onchocerciasis has been classified as one of the Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTDs) by WHO. More than 99% of infected people live in 31 African countries. The disease also exists in some foci in Latin America and Yemen.
About half a million people are blind or visually impaired due to the disease which is caused by a parasitic worm living under the skin in humans, spread by black fly bites. Onchocerciasis is a chronic systemic disease capable of causing extensive and disfiguring skin disease, chronic itching, musculoskeletal complaints, weight loss, alteration in host immune responses and possibly epilepsy and growth impairment
A clinical expert collaborating with Niramai, Professor Dr Christopher L King from The Centre for Global Health and Diseases, Cleveland, said, “Onchocerciasis, more commonly known as river blindness, is the world’s second leading infectious cause of blindness. Niramai technology can be a valuable tool to detect infectious live worms in a non-invasive way and help with the global effort to eliminate this very disabling disease.”
About half a million people are blind or visually impaired due to the disease which is caused by a parasitic worm living under the skin in humans, spread by black fly bites. In addition to blinding, onchocerciasis is a chronic systemic disease capable of causing extensive and disfiguring skin disease, chronic itching, musculoskeletal complaints, weight loss, alteration in host immune responses and possibly epilepsy and growth impairment.
There is no vaccine or medication to prevent infection with O. volvulus. Mass administration of ivermectin, a drug which kills microfilariae and prevents their release by the adult worms for several months is the recommended treatment but annual treatments are required. A new powerful drug to combat river blindness called moxidectin is undergoing trials.
Dr Geetha Manjunath, CEO & CTO, Niramai, said, “We are very excited to collaborate with Gates Foundation to extend the application of our innovative technique to areas other than breast cancer. Successful completion of this research project will demonstrate a breakthrough result of Thermalytix™ being a new way of sensing many abnormalities in human body in a non-invasive, radiation-free and accurate way, even beyond cancer!”