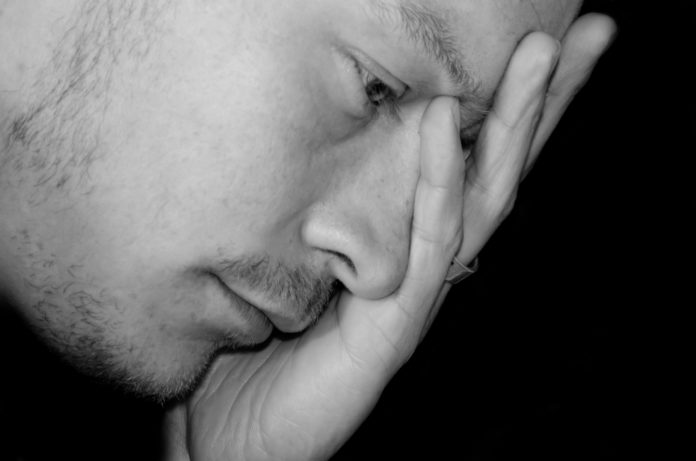
The mystery of why anti-depressants do not work equally well in all patients may finally have been solved.
Researchers from University Medical Center Mainz and the Max Planck Institute of Psychiatry in Germany have identified blood signatures associated with response to antidepressant treatment and could show the importance of the stress-related glucocorticoid receptor in recovery from depression. Glucocorticoids are a class of hormones that have a very important role to play in situations of stress.

Major depression is the leading cause of disability according to the World Health Organization, affecting an estimated 350 million people worldwide, but only one-third of patients benefit from the first antidepressant prescribed. In India World Health Organisation estimates there are some 5 crore people suffering from depression. Although the currently available treatments are safe, there is significant variability in the outcome of antidepressant treatment. So far there are no clinical assessments that can predict with a high degree of certainty whether a particular patient will respond to a particular antidepressant.
To tackle this challenge, scientists established a novel experimental approach in animals focusing on extreme phenotypes in response to antidepressant treatment. This model simulated the clinical situation, by identifying good and poor responders to antidepressant treatment. They hypothesised that conditions in the mouse model would facilitate the identification of valid peripheral biomarkers for antidepressant treatment response and could potentially apply to humans.
“We were able to identify a cluster of antidepressant response-associated genes in the mouse model that we then validated in a cohort of depressed patients from our collaborators from Emory University, Atlanta,” said Tania Carrillo-Roa from the Max Planck Institute of Psychiatry. Finding the most effective antidepressant medication for each patient depends on trial and error. That is why the urgent need to establish conceptually novel strategies for the identification of biomarkers associated with a positive response.
Additional analyses indicated that the glucocorticoid receptor, which is one of the most important players in fine-tuning the stress hormone system, shapes the response to antidepressant treatment. Ultimately, identification of biomarkers predictive of individual responses to treatment would dramatically improve the quality of care/ treatment for depressed patients by taking the trial and error out of prescribing antidepressants.