Experts discover a protein which triggers fat burn without exercise
Many people make New Year’s resolutions to hit the gym and get into shape. But do you know how exercise helps you to lose weight?
A study published by Cell Press says, a signaling molecule called interleukin-6 plays a critical role in the fat burning process. The study involved a 12-week intervention consisting of bicycle exercise decreased visceral abdominal fat in obese adults. Surprisingly, however, this positive effect was nonexistent among participants who were treated with tocilizumab, a drug that blocks interleukin-6 signaling.
“The take home for the general audience is ‘do exercise,'” says author Anne-Sophie Wedell-Neergaard of the University of Copenhagen. “We all know that exercise promotes better health, and now we also know that regular exercise training reduces abdominal fat mass and thereby potentially also the risk of developing cardio-metabolic diseases.”
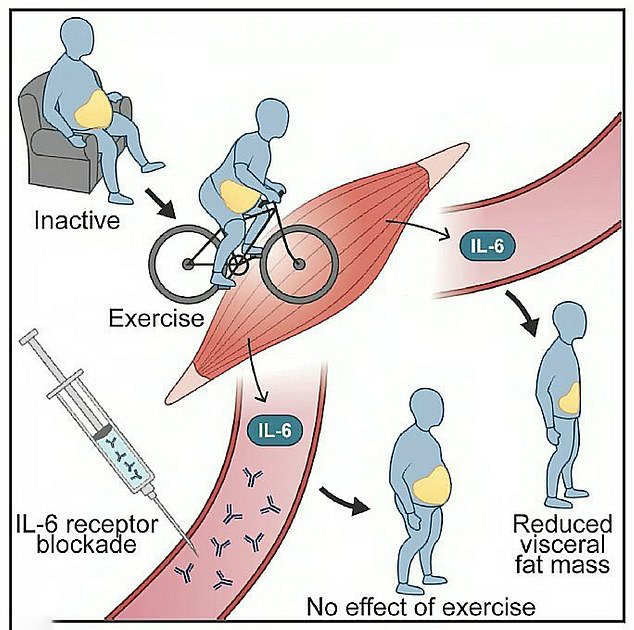
The fat studied by Ms Wedell-Neergaard and her team was visceral fat – which builds up around the internal organs and can trigger disease. People taking the interleukin-6 blocking drug ended up with higher cholesterol, suggesting the protein could also be used for people with high cholesterol levels. But the researchers said their discovery was no excuse for people to sit around waiting for a miracle jab, and urged people to be active.
We all know that exercise promotes better health, and now we also know that regular exercise training reduces abdominal fat mass and thereby potentially also the risk of developing cardio-metabolic diseases
The scientists suspected interleukin-6 was involved in losing fat because it regulates energy metabolism. It also stimulates the breakdown of fats in healthy people, and is released from skeletal muscle during exercise. But unhealthy people – such as those with severe obesity, type 2 diabetes and heart disease – also have naturally higher levels of interleukin-6.
The authors note that the study was exploratory and not intended to evaluate a given treatment in a clinical setting. To complicate matters, interleukin-6 can have seemingly opposite effects on inflammation, depending on the context. For example, chronic low-grade elevations of interleukin-6 are seen in patients with severe obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. “The signaling pathways in immune cells versus muscle cells differ substantially, resulting in pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory actions, so interleukin-6 may act differently in healthy and diseased people,” Wedell-Neergaard explains.
“It is important to stress that when you start exercising, you may increase body weight due to increased muscle mass. So, in addition to measuring your overall body weight, it would be useful, and maybe more important, to measure waist circumference to keep track of the loss of visceral fat mass and to stay motivated.”